High level views
The diagram below depicts a simplified architectural layout of the CDK FEP config and indicates at a high level how components communicate.
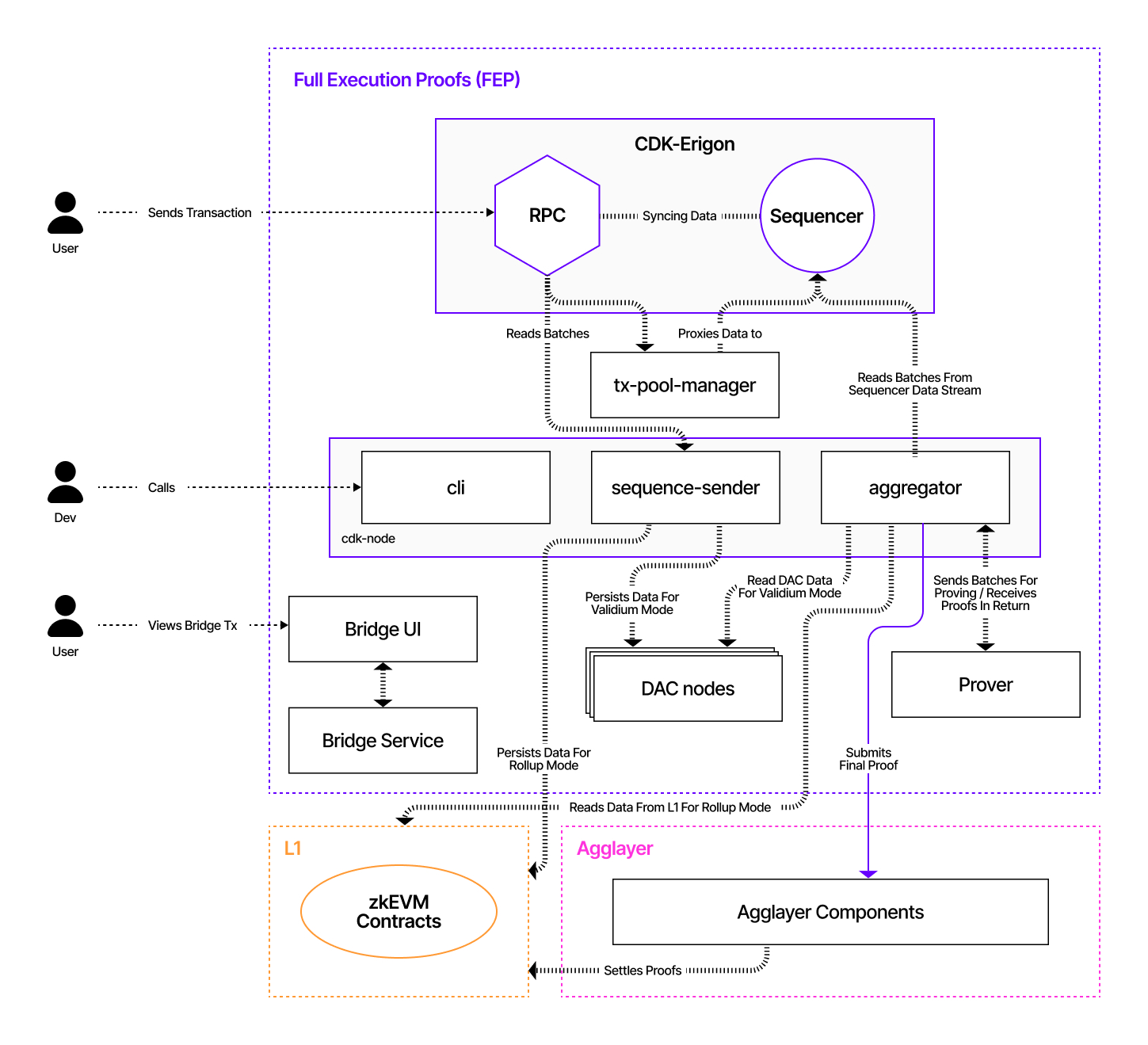
Component Interactions¶
- The CLI tool is the starting point. Developers, or chain administrators in particular, use the CLI tool to build and configure chains in various modes of operation, such as validiums and rollups.
- Once a chain is configured with the CLI, users can submit transactions through the CDK Erigon RPC node. These transactions are relayed to the
tx-pool managerbefore the sequencer selects and executes them. - The sequencer sequences transaction batches and synchronizes data with the RPC node.
- The sequencer sender reads batch data from the RPC node.
- The aggregator reads batch data from the sequencer data stream.
- The sequencer sender persists data into the L1 smart contract domain for rollup mode and into DAC nodes for validium mode operations.
- The aggregator sends batches to the prover and receives proofs in return. Together with the prover, it aggregates the proofs into batches before submitting the final proofs to the Agglayer or L1, depending on the chosen settlement layer.
- Users interact with the bridge service via the bridge UI or API.
- The Agglayer verifies proofs and interacts with the L1 smart contracts.
User Data Flow¶
The following diagram sequentially depicts the user data flow for the CDK FEP config in validium mode using a mock prover and an Agglayer connection.
Sequential Interactions¶
- The user sends a transaction to the CDK Erigon RPC node.
- The CDK Erigon RPC node proxies the data to the CDK Erigon sequencer node and syncs the batch data between the sequencer and the RPC nodes.
- The sequencer sequences the transaction batches.
- The sequencer sender reads batches from the RPC node.
- In validium mode only, the sequencer sender persists transaction data into the DAC nodes.
- The sequencer sender sequences the batches into the L1 smart contracts.
- The aggregator reads batches from the sequencer data stream.
- The aggregator sends batches to the provers.
- The aggregator submits the final proof to the Agglayer.
- The Agglayer submits the final proof to the L1 smart contract domain.
Mermaid Sequence Diagram¶
sequenceDiagram
participant User
participant ErigonRPC as CDK Erigon RPC Node
participant Sequencer as CDK Erigon Sequencer Node
participant SeqSender as Sequencer Sender
participant Aggregator
participant Agglayer
participant DACNodes as DAC Nodes
participant Prover
participant L1 as L1 Smart Contracts
User->>ErigonRPC: Send transaction
ErigonRPC->>Sequencer: Proxy and sync transaction data
Sequencer->>Sequencer: Sequence transaction batches
SeqSender->>ErigonRPC: Read batches
SeqSender->>DACNodes: Persist transaction data (validium mode only)
SeqSender->>L1: Sequence batches into L1 Smart Contracts
Aggregator->>Prover: Send batches to Prover
Prover->>Aggregator: Return proofs
Aggregator->>Aggregator: Aggregate proofs
Aggregator->>Agglayer: Submit final proof
Agglayer->>L1: Submit final proof to L1 Smart Contract Domain