Checkpoints
Checkpoints are vital components of the Polygon network, representing snapshots of the Bor chain state. These checkpoints are attested by a majority of the validator set before being validated and submitted on Ethereum contracts.
Heimdall, an integral part of this process, manages checkpoint functionalities using the checkpoint module. It coordinates with the Bor chain to verify checkpoint root hashes when a new checkpoint is proposed.
Checkpoint life-cycle and types¶
Life-cycle¶
Heimdall selects the next proposer using Tendermint’s leader selection algorithm. The multi-stage checkpoint process is crucial due to potential failures when submitting checkpoints on the Ethereum chain caused by factors like gas limit, network traffic, or high gas fees.
Each checkpoint has a validator as the proposer. The outcome of a checkpoint on the Ethereum chain (success or failure) triggers an ack (acknowledgment) or no-ack (no acknowledgment) transaction, altering the proposer for the next checkpoint on Heimdall.
Flow chart representations¶
Types and structures¶
Checkpoint block header¶
type CheckpointBlockHeader struct {
Proposer types.HeimdallAddress `json:"proposer"`
StartBlock uint64 `json:"startBlock"`
EndBlock uint64 `json:"endBlock"`
RootHash types.HeimdallHash `json:"rootHash"`
AccountRootHash types.HeimdallHash `json:"accountRootHash"`
TimeStamp uint64 `json:"timestamp"`
}
Root hash calculation¶
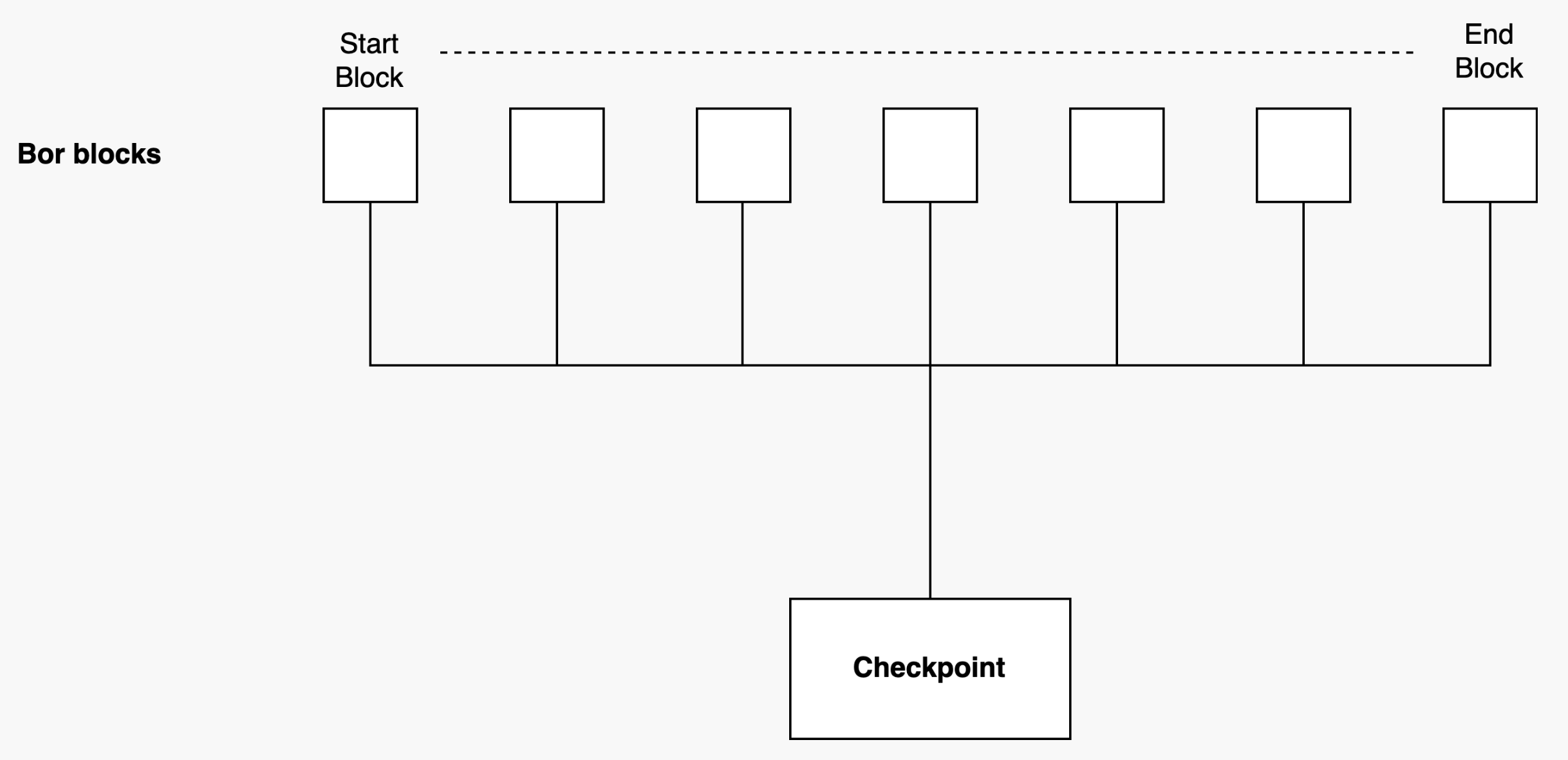
The RootHash is calculated as a Merkle hash of Bor block hashes from StartBlock to EndBlock. The process involves hashing each block’s number, time, transaction hash, and receipt hash, then creating a Merkle root of these hashes.
blockHash = keccak256([number, time, tx hash, receipt hash])
Pseudocode for the root hash for 1 to n Bor blocks:
B(1) := keccak256([number, time, tx hash, receipt hash])
B(2) := keccak256([number, time, tx hash, receipt hash])
.
.
.
B(n) := keccak256([number, time, tx hash, receipt hash])
// checkpoint is Merkle root of all block hash
checkpoint's root hash = Merkel[B(1), B(2), ....., B(n)]
Here are some snippets of how checkpoint is created from Bor chain block headers.
Source: https://github.com/maticnetwork/heimdall/blob/develop/checkpoint/types/merkel.go#L60-L114
// Golang representation of block data used in checkpoint
blockData := crypto.Keccak256(appendBytes32(
blockHeader.Number.Bytes(),
new(big.Int).SetUint64(blockHeader.Time).Bytes(),
blockHeader.TxHash.Bytes(),
blockHeader.ReceiptHash.Bytes(),
))
// array of block hashes of Bor blocks
headers := [blockData1, blockData2, ..., blockDataN]
// merkel tree
tree := merkle.NewTreeWithOpts(merkle.TreeOptions{EnableHashSorting: false, DisableHashLeaves: true})
tree.Generate(convert(headers), sha3.NewLegacyKeccak256())
// create checkpoint's root hash
rootHash := tree.Root().Hash
AccountRootHash¶
AccountRootHash is the hash of the validator account-related information that needs to pass to the Ethereum chain at each checkpoint.
eachAccountHash := keccak256([validator id, withdraw fee])
Pseudocode for the account root hash for 1 to n Bor blocks:
B(1) := keccak256([validator id, withdraw fee])
B(2) := keccak256([validator id, withdraw fee])
.
.
.
B(n) := keccak256([validator id, withdraw fee])
// account root hash is Merkle root of all block hash
checkpoint's account root hash = Merkel[B(1), B(2), ....., B(n)]
Golang code for the account hash can be found here: https://github.com/maticnetwork/heimdall/blob/develop/types/dividend-account.go
// DividendAccount contains burned Fee amount
type DividendAccount struct {
User HeimdallAddress `json:"user"`
FeeAmount string `json:"feeAmount"` // string representation of big.Int
}
// CalculateHash hashes the values of a DividendAccount
func (da DividendAccount) CalculateHash() ([]byte, error) {
fee, _ := big.NewInt(0).SetString(da.FeeAmount, 10)
divAccountHash := crypto.Keccak256(appendBytes32(
da.User.Bytes(),
fee.Bytes(),
))
return divAccountHash, nil
}
Messages in checkpoint module¶
MsgCheckpoint¶
MsgCheckpoint handles checkpoint verification on Heimdall, utilizing RLP encoding for Ethereum chain verification. It prioritizes transactions with high gas consumption to ensure only one MsgCheckpoint transaction per block.
// MsgCheckpoint represents checkpoint transaction
type MsgCheckpoint struct {
Proposer types.HeimdallAddress `json:"proposer"`
StartBlock uint64 `json:"startBlock"`
EndBlock uint64 `json:"endBlock"`
RootHash types.HeimdallHash `json:"rootHash"`
AccountRootHash types.HeimdallHash `json:"accountRootHash"`
}
MsgCheckpointAck¶
MsgCheckpointAck manages successful checkpoint submissions, updating the checkpoint count and clearing the checkpointBuffer.
// MsgCheckpointAck represents checkpoint ack transaction if checkpoint is successful
type MsgCheckpointAck struct {
From types.HeimdallAddress `json:"from"`
HeaderBlock uint64 `json:"headerBlock"`
TxHash types.HeimdallHash `json:"tx_hash"`
LogIndex uint64 `json:"log_index"`
}
MsgCheckpointNoAck¶
MsgCheckpointNoAck deals with unsuccessful checkpoints or offline proposers, allowing a timeout period before selecting a new proposer.
// MsgCheckpointNoAck represents checkpoint no-ack transaction
type MsgCheckpointNoAck struct {
From types.HeimdallAddress `json:"from"`
}
Parameters and CLI commands¶
Parameters¶
The checkpoint module contains the following parameters:
| Key | Type | Default value |
|---|---|---|
| CheckpointBufferTime | uint64 | 1000 * time.Second |
CLI commands¶
Commands are available for various actions such as sending checkpoints, sending ack or no-ack transactions, and querying parameters.
Printing all parameters¶
heimdallcli query checkpoint params --trust-node
Expected Result:
checkpoint_buffer_time: 16m40s
Send Checkpoint¶
Following command sends checkpoint transaction on Heimdall:
heimdallcli tx checkpoint send-checkpoint \
--start-block=<start-block> \
--end-block=<end-block> \
--root-hash=<root-hash> \
--account-root-hash=<account-root-hash> \
--chain-id=<chain-id>
Send ack¶
Following command sends ack transaction on Heimdall if checkpoint is successful on Ethereum:
heimdallcli tx checkpoint send-ack \
--tx-hash=<checkpoint-tx-hash>
--log-index=<checkpoint-event-log-index>
--header=<checkpoint-index> \
--chain-id=<chain-id>
Send no-ack¶
Following command send no-ack transaction on Heimdall:
heimdallcli tx checkpoint send-noack --chain-id <chain-id>
REST APIs¶
Heimdall provides several REST APIs for interacting with the checkpoint module, including endpoints for preparing messages, querying checkpoints, and more.
| Name | Method | Endpoint |
|---|---|---|
| It returns the prepared msg for ack checkpoint | POST | /checkpoint/ack |
| It returns the prepared msg for new checkpoint | POST | /checkpoint/new |
| It returns the prepared msg for no-ack checkpoint | POST | /checkpoint/no-ack |
| Checkpoint by number | GET | /checkpoints/<checkpoint-number> |
| Get current checkpoint buffer state | GET | /checkpoints/buffer |
| Get checkpoint counts | GET | /checkpoints/count |
| Get last no-ack details | GET | /checkpoints/last-no-ack |
| Get latest checkpoint | GET | /checkpoints/latest |
| All checkpoints | GET | /checkpoints/list |
| It returns the checkpoint parameters | GET | /checkpoints/parama |
| It returns the prepared checkpoint | GET | /checkpoints/prepare |
| Get ack count, buffer, validator set, validator count and last-no-ack details | GET | /overview |
For more details and the response format of these APIs, visit Heimdall API Documentation.