CDK rollup
Polygon zkEVM is a zero-knowledge rollup (or zk-rollup) designed to emulate the Ethereum Virtual Machine.
It is a scaling-solution to Ethereum as it rolls up many transactions into one batch.
These batches are submitted to the L1, where their integrity is proved and verified before being included in the L1 state.
Proving, verification of batches, and state changes are all controlled by smart contracts.
Most important to understand is the primary path taken by transactions from when users submit these transactions to the zkEVM network up until they are finalized and incorporated in the L1 State.
Polygon zkEVM achieves this by utilizing several actors. The diagram below depicts the various actors and how they interact.
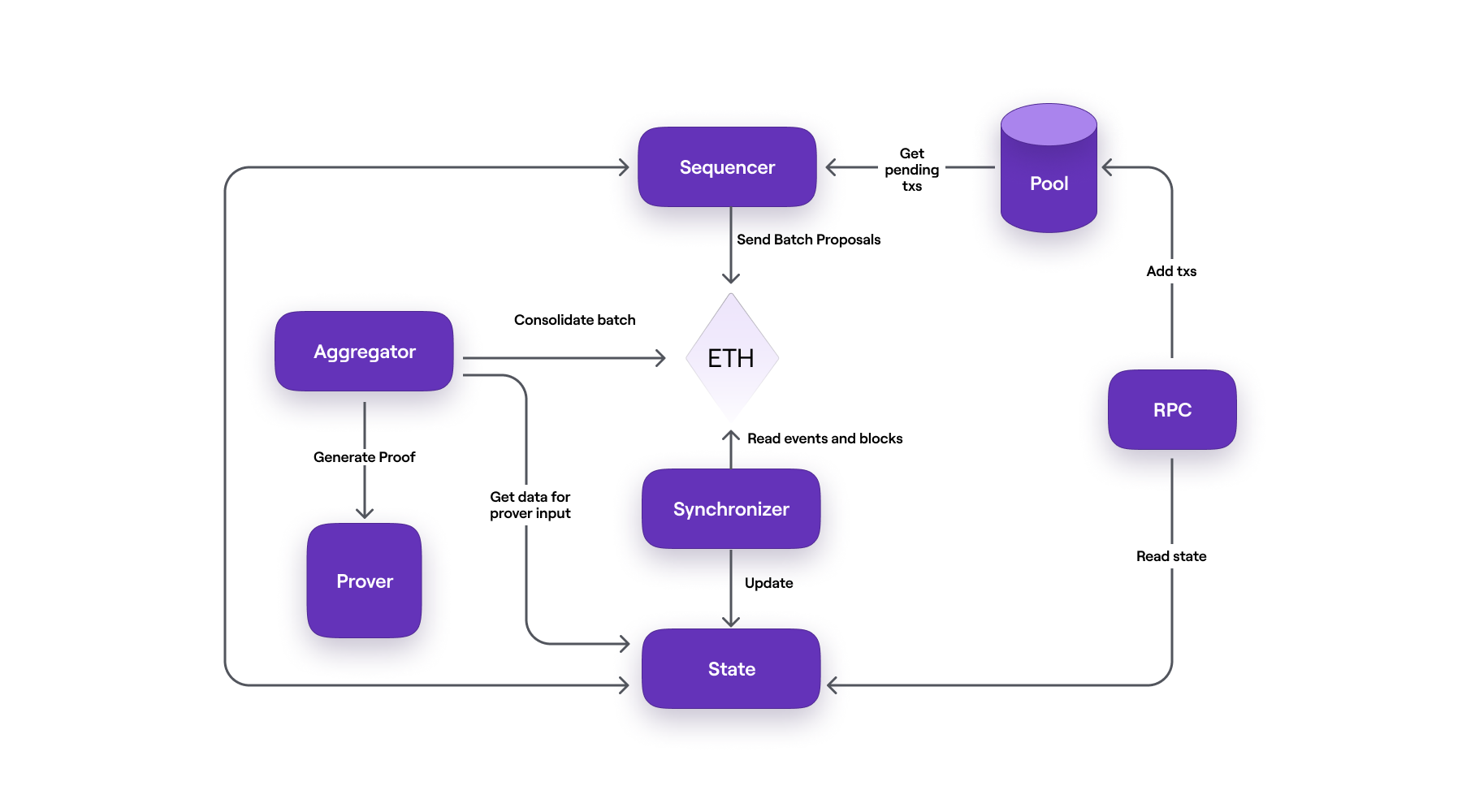
Here is an outline of the most prominent rollup components:
- The users, who connect to the zkEVM network by means of an RPC node (e.g., Infura or Alchemy), submit their transactions to a database called the pool DB.
- The pool DB is the storage for transactions submitted by users. These are kept in the pool waiting to be put in a batch by the sequencer.
- The sequencer is a node responsible for fetching transactions from the pool DB, checking if the transactions are valid, then putting valid ones into a batch. The sequencer submits all batches to the L1 and then sequences the batches. This process proposes the sequence of batches to be included in the L1 state.
- The state DB is a database for permanently storing state data (but not the Merkle trees).
- The synchronizer is the component that updates the state DB by fetching data from Ethereum through the Etherman.
- The Etherman is a low-level component that implements methods for all interactions with the L1 network and smart contracts.
- The aggregator is another node whose role is to produce proofs attesting to the integrity of the sequencer’s proposed state-change. These proofs are zero-knowledge proofs (or ZK-proofs) and the aggregator employs a cryptographic component called the prover for this purpose.
- The prover is a complex cryptographic tool capable of producing ZK-proofs of hundreds of batches, and aggregating these into a single ZK-proof which is published as the validity proof.