Asset Bridging
Learn how to bridge tokens and native assets between different chains using the Unified Bridge
Overview
Asset bridging enables the transfer of tokens and native assets between Agglayer connected chains. The Unified Bridge supports various token types and provides a secure, trustless mechanism for cross-chain asset transfers.
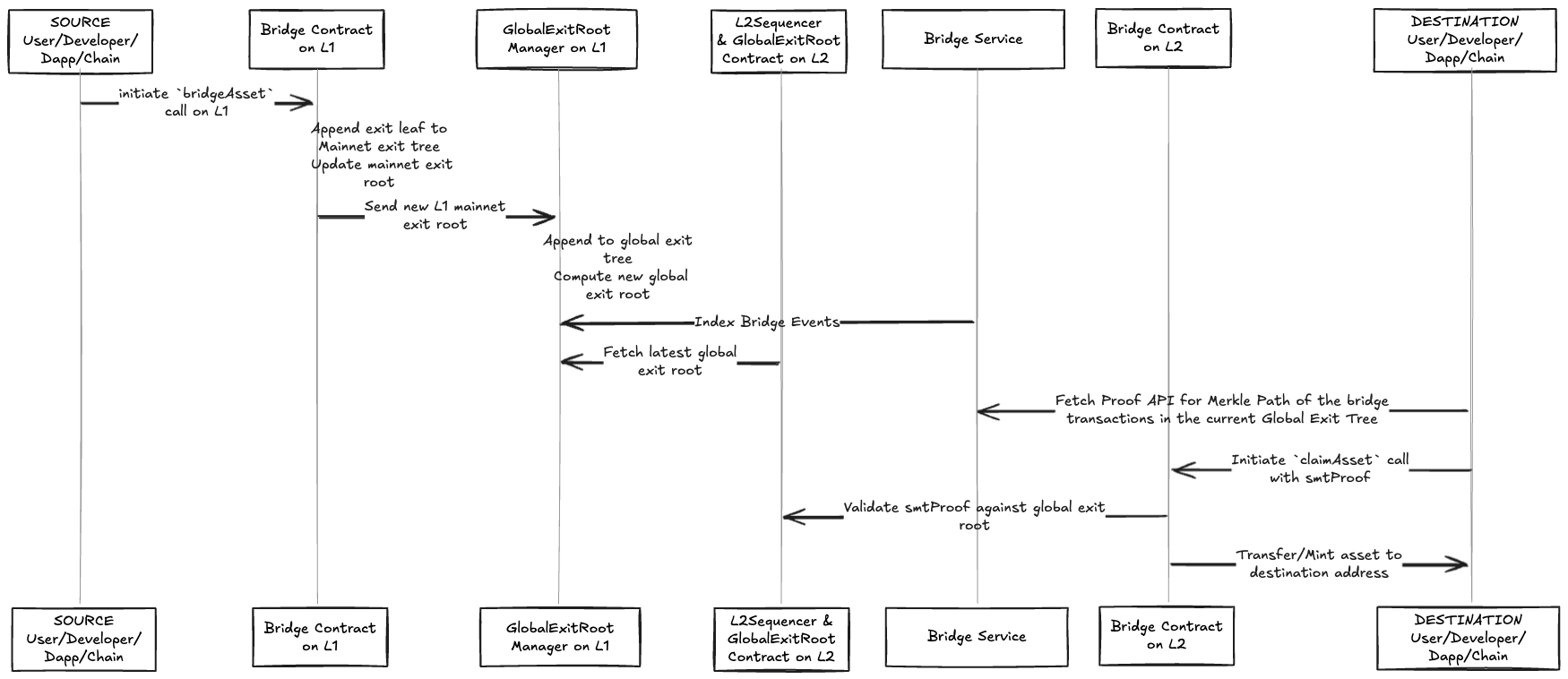
Figure 1: Complete asset bridging flow from L1 to L2
Supported Token Types
The Unified Bridge handles different token types with specific mechanisms:
| Token Type | Source Chain Action | Destination Chain Action |
|---|---|---|
| Native Gas Token (ETH, Custom Gas Token) | Bridge contract holds tokens | Bridge contract transfers tokens |
| WETH | Burn WETH tokens from user | Mint WETH tokens to user |
| Foreign ERC20 (Not native to source) | Burn ERC20 tokens from user | Mint wrapped tokens to user |
| Native ERC20 (Native to source) | Transfer ERC20 to bridge contract | Transfer from bridge contract to user |
Bridge Asset Function
The bridgeAsset function initiates asset transfers between chains.
Function Signature
function bridgeAsset(
uint32 destinationNetwork,
address destinationAddress,
uint256 amount,
address token,
bool forceUpdateGlobalExitRoot,
bytes calldata permitData
) external payableParameters
destinationNetwork: Network ID of the destination chaindestinationAddress: Address to receive assets on destination chainamount: Amount of tokens to bridgetoken: Token contract address (0x0 for native gas token)forceUpdateGlobalExitRoot: Whether to update GER immediatelypermitData: Raw permit data for ERC20 tokens (optional)
Process Steps
- Validation: Check destination network is not the source network
- Token Preparation: Handle token based on type (lock, burn, or transfer)
- Event Emission: Emit
BridgeEventwith transaction details - Tree Update: Add transaction to Local Exit Tree as leaf node
Token Preparation Logic
The bridge handles different token types with specific mechanisms based on their origin and nature:
Note that in case
ETHis the native token, WETHToken will be at0x0address.
Native Gas Token (ETH, Custom Gas Token)
// Bridge contract holds the tokens
// The native gas token is already transferred via msg.value
// No additional token transfer requiredWETH Token
// Burn WETH tokens from user's address
IWETH(token).burnFrom(msg.sender, amount);Foreign ERC20 Token (Not native to source chain)
// If the token contract is not originally from the source network,
// burn the ERC20 token from user's address
IERC20(token).burnFrom(msg.sender, amount);Native ERC20 Token (Native to source chain)
// If the token contract is originally from the source network:
// 1. Execute permit if provided
if (permitData.length > 0) {
IERC20Permit(token).permit(...);
}
// 2. Transfer tokens from user to bridge contract
IERC20(token).transferFrom(msg.sender, address(this), amount);Claim Asset Function
The claimAsset function claims bridged assets on the destination chain.
Function Signature
function claimAsset(
bytes32[_DEPOSIT_CONTRACT_TREE_DEPTH] calldata smtProofLocalExitRoot,
bytes32[_DEPOSIT_CONTRACT_TREE_DEPTH] calldata smtProofRollupExitRoot,
uint256 globalIndex,
bytes32 mainnetExitRoot,
bytes32 rollupExitRoot,
uint32 originNetwork,
address originTokenAddress,
uint32 destinationNetwork,
address destinationAddress,
uint256 amount,
bytes calldata metadata
) externalParameters
smtProofLocalExitRoot: Merkle proof for Local Exit RootsmtProofRollupExitRoot: Merkle proof for Rollup Exit RootglobalIndex: Global index identifying the transactionmainnetExitRoot: Mainnet Exit Root at time of transactionrollupExitRoot: Rollup Exit Root at time of transactionoriginNetwork: Network ID of source chainoriginTokenAddress: Token address on source chaindestinationNetwork: Network ID of destination chaindestinationAddress: Address to receive assetsamount: Amount of tokens to claimmetadata: Additional metadata (if any)
Process Steps
- Validation: Verify destination network matches current chain
- Proof Verification: Verify Merkle proofs against Global Exit Root
- Duplicate Check: Ensure transaction hasn't been claimed before
- Token Transfer: Transfer tokens based on token type (see Token Transfer Logic below)
- Claim Record: Mark transaction as claimed
Token Transfer Logic
Once the proof verification passes, the bridge claims tokens using different mechanisms based on the token type:
| Token type | Action |
|---|---|
| ETH is gas token | Bridge contract transfers the amount from itself to the destination address |
| WETH where ETH is not gas token | Mint new WETH tokens to the destination address |
| Custom gas token | Bridge contract transfers the amount from itself to the destination address |
| Native ERC20 Token | If the token contract is originally from this destination network, transfer the ERC20 token from bridge contract to destination address |
| Foreign ERC20 Token, First time bridging | Deploy a new ERC20 Token contract to host this new Foreign ERC20 Token, and mint the transfer amount to destination address |
| Foreign ERC20 Token, Contract exists | Mint the transfer amount to destination address |
Proof Verification Logic
// Construct Global Exit Root
bytes32 globalExitRoot = keccak256(abi.encodePacked(mainnetExitRoot, rollupExitRoot));
// Verify against synchronized GER
require(globalExitRoot == getGlobalExitRoot(), "Invalid global exit root");
// Verify Merkle proofs based on origin
if (originNetwork == 0) {
// L1 to L2: Verify against mainnet exit root
verifyMerkleProof(smtProofLocalExitRoot, mainnetExitRoot, globalIndex);
} else {
// L2 to L2: Verify against rollup exit root
verifyMerkleProof(smtProofLocalExitRoot, rollupExitRoot, globalIndex);
verifyMerkleProof(smtProofRollupExitRoot, rollupExitRoot, globalIndex);
}Bridging Flows
L1 to L2 Bridging
L2 to L1 Bridging
L2 to L2 Bridging
Last updated on